Tardive dyskinesia (TD), a hyperkinetic movement disorder caused by antipsychotics, affects multiple aspects of patients’ lives and undermines the stability of their underlying mental health disorders.1,2 Even mild symptoms can have a significant impact extending into social, psychological, and emotional aspects of patients’ lives.3,4 The prevalence of TD is growing, owing to the increased use of antipsychotics for patients with mood disorders. These patients tend to have a greater awareness of abnormal movements and the impact they have on their lives.2,7,8 The American Psychiatric Association (APA) Guidelines recommend vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2) inhibitors for the treatment for TD if it has an impact on the patient, regardless of the severity of movements.9 Additionally, VMAT2 inhibitors are recommended for the treatment of TD without the need to modify the antipsychotic dose.9-11
AUSTEDO XR is a VMAT2 inhibitor approved in the US for the treatment of adults with TD.11 This article reviews efficacy and safety data from the pivotal and long-term, open-label extension (OLE) studies. Then it delves into key findings from a real-world survey that evaluated patients’ experience with AUSTEDO XR, including perceived ease of use and effects on social and emotional well-being.
The efficacy and safety of AUSTEDO in the treatment of TD was evaluated in 2 pivotal clinical trials, ARM-TD (Aim to Reduce Movements in Tardive Dyskinesia) and AIM-TD (Addressing Involuntary Movements in Tardive Dyskinesia).12,13
ARM-TD was a 12-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in which doses of AUSTEDO were titrated to an individualized dose that reduced abnormal movements and was tolerated. After screening, patients were randomized 1:1 to receive AUSTEDO twice daily (BID) or placebo.13
AIM-TD was a 12-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in which patients received AUSTEDO 0 mg (placebo), 12 mg/day, 24 mg/day, or 36 mg/day.11,12
The primary efficacy endpoint in both trials was the change in Abnormal Involuntary Movement Scale (AIMS) total score from baseline to Week 12.6,11-13
Patients who received AUSTEDO demonstrated a rapid response as early as Week 2 and achieved a significant and meaningful reduction in TD severity at Week 12.6,11,13 In ARM-TD, patients receiving AUSTEDO demonstrated a statistically significant improvement in AIMS total score, with a reduction of 3.0 points from baseline to Week 12, compared with 1.6 points in the placebo group (treatment effect of -1.4 points, P=0.019) (Figure 1).6,13 At Week 12, 94% of patients were taking a dose of ≥30 mg/day.6
At Week 12 in AIM-TD, AIMS total score was reduced by 3.3 points from baseline in patients taking AUSTEDO 36 mg/day vs 1.4 points in patients taking placebo (treatment effect of -1.9 points, P=0.001).11,12
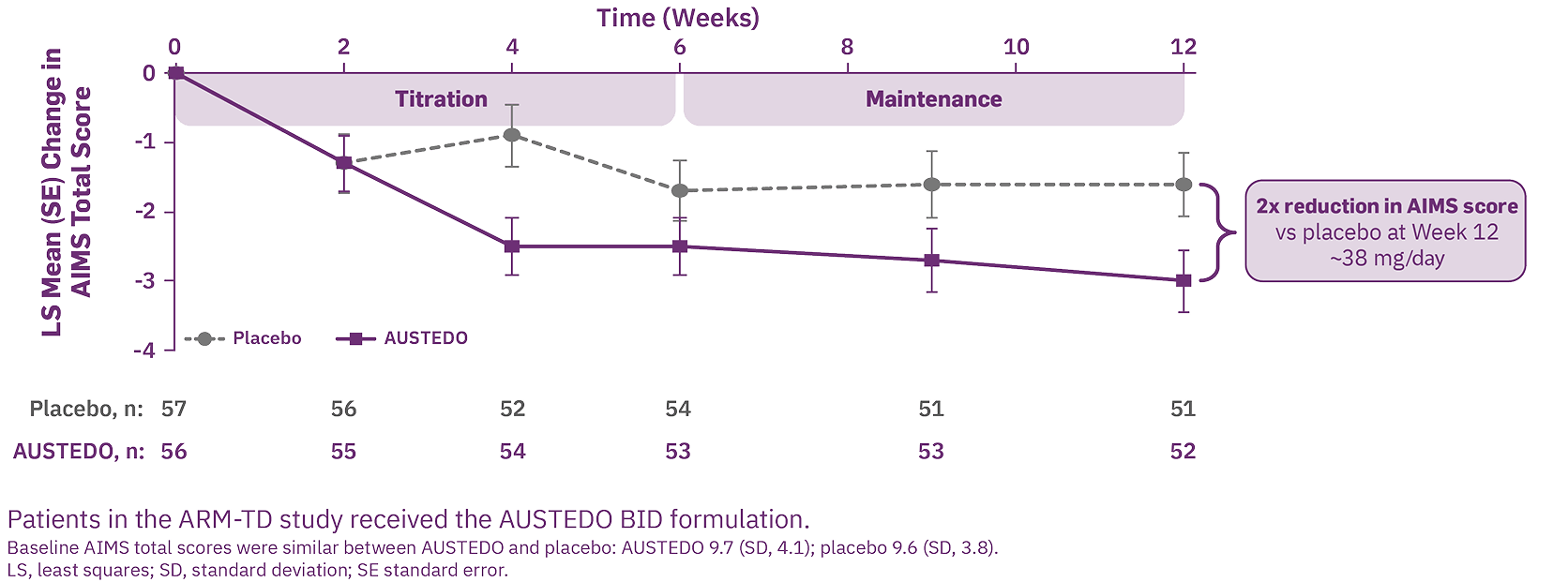
RIM-TD (Reducing Involuntary Movements in Participants With Tardive Dyskinesia) was an open-label study designed to evaluate long-term treatment of TD with AUSTEDO for up to 3 years, following completion of ARM-TD or AIM-TD. Among the patients evaluated, 337 patients were in treatment at baseline and 160 patients remained on treatment through the end of Week 145.14 The mean overall compliance rate was nearly 90% at 3 years.6
At Week 145, 87% of patients were taking a dose of ≥30 mg/day.6
At baseline, concurrent diagnoses included schizophrenia (50%), schizoaffective disorder (10%), bipolar disorder (17%), and depression (19%).6
Increasing improvement in AIMS total score was observed over 3 years in the OLE study.14 Specifically, 71% of patients at Week 145 saw improvement relative to Week 15 (Figure 2).6
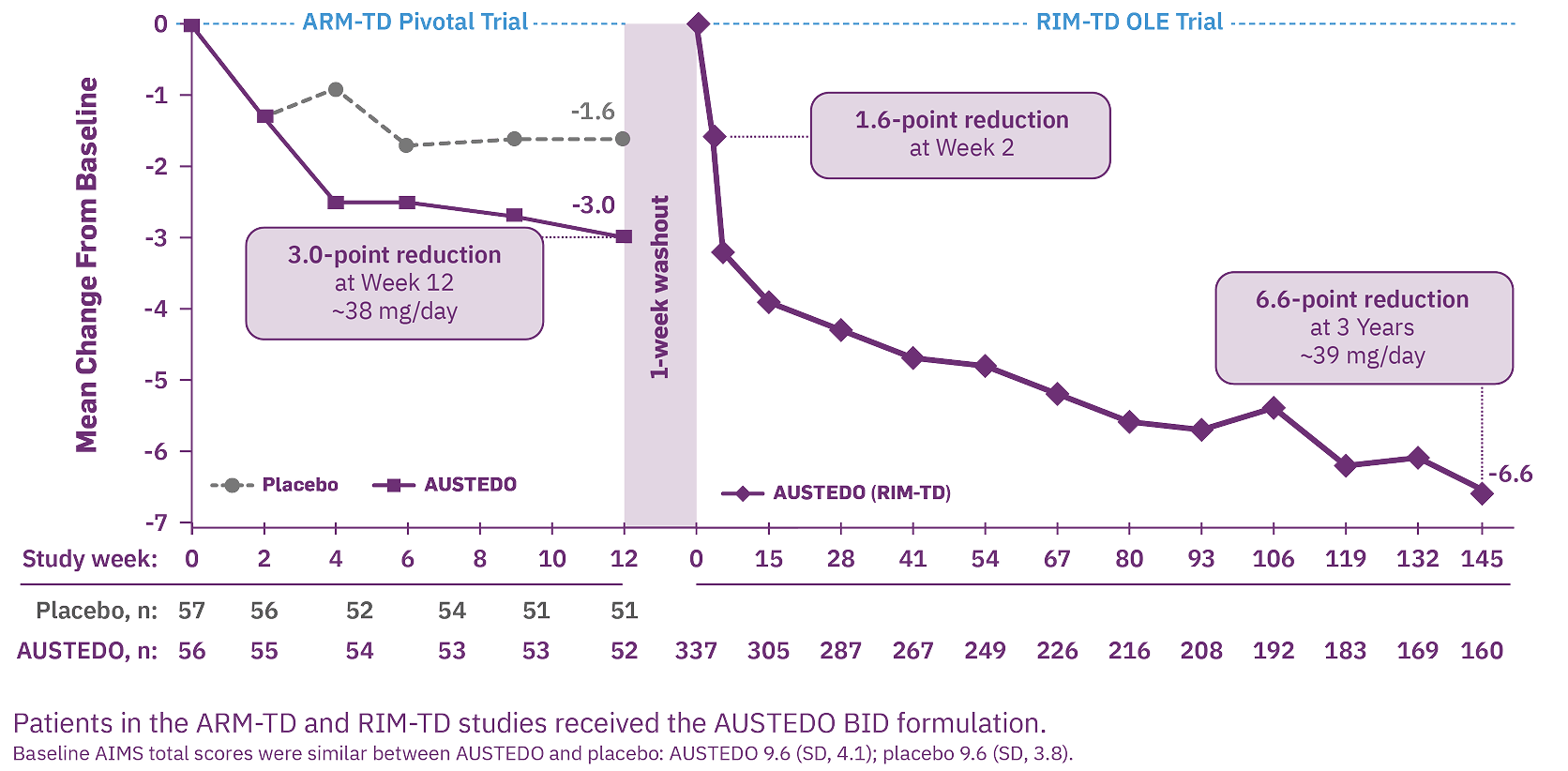
Consistent outcomes were observed, regardless of the underlying condition.6
Across both placebo-controlled studies in patients with TD, the most common adverse reactions reported in patients treated with AUSTEDO (>3% and greater than placebo) were nasopharyngitis and insomnia.11 The adverse reactions occurring in patients treated with AUSTEDO (12-48 mg per day) (≥2%) are summarized in Figure 3.
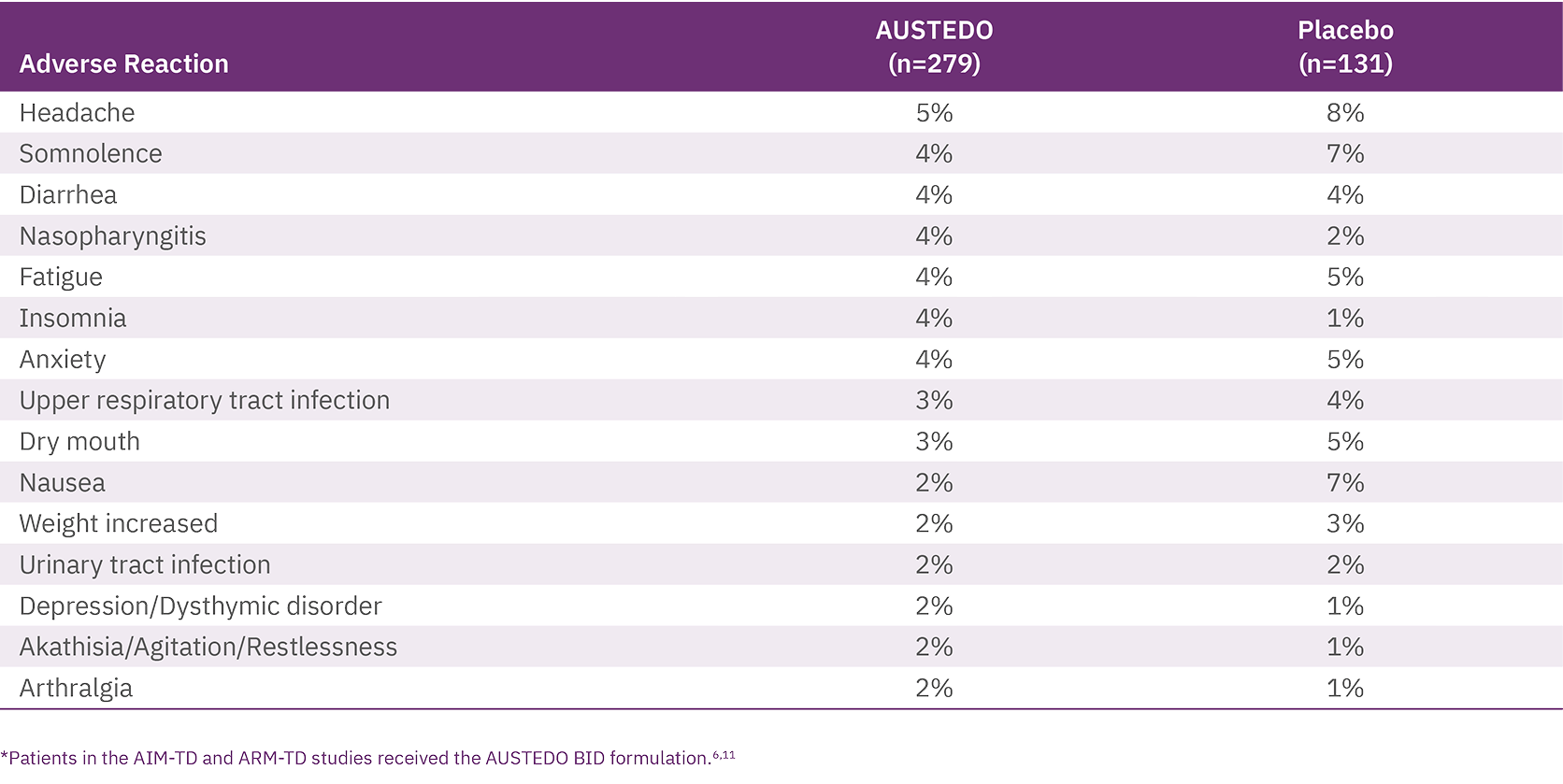
Discontinuation due to adverse events (AEs) occurred in 4% of patients taking AUSTEDO compared with 3% of patients treated with placebo.12 Four percent of patients required dose reduction of AUSTEDO due to AEs compared with 2% of patients taking placebo.11 Once patients were titrated to their maintenance dose, several AEs were no longer reported, including dry mouth and nausea in AIM-TD and somnolence and dry mouth in ARM-TD.6
No new safety signals were identified in RIM-TD, and AEs were comparable with those in the 12-week clinical trials.14 Results were consistent across patient subgroups, including those with psychotic disorders such as schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder, as well as those with mood disorders like depression and bipolar disorder, and other disorders.15
Adverse reactions with AUSTEDO XR are expected to be similar to AUSTEDO BID.11
A prospective, cross-sectional survey of 118 patients with TD was conducted between July 2, 2024, and August 2, 2024, to assess patients’ experience with AUSTEDO XR, including perceived ease of use and effects on social and emotional well-being. Interim results from this survey found that more than 50% of patients reported improved social and emotional well-being as a result of movement reduction with AUSTEDO XR. Patients reported greater self-esteem (66%), less embarrassment (73%) and anxiety (59%), and better overall emotional well-being (77%) (Figure 4). In addition, 98% of patients said taking once-daily AUSTEDO XR was easy, and 95% planned to continue taking AUSTEDO XR.16

It is crucial to consider patient comorbidities and the medications they may be taking, as the potential exists for drug interactions when selecting a VMAT2 inhibitor. AUSTEDO XR is metabolized primarily by CYP2D6, with minor contributions from CYP3A4/5 and other enzymes to form several minor metabolites.11 However, there are no dose restrictions up to 36 mg/day for patients starting AUSTEDO XR (Figure 5).11 Moreover, no dose adjustments to P-gp substrates, which may include some calcium channel blockers, statins, and antimicrobials, are required when taking AUSTEDO XR.11,17

AUSTEDO XR is the only VMAT2 inhibitor indicated for TD with no recommendations against concomitant use with strong CYP3A4/5 inducers or inhibitors.11,18
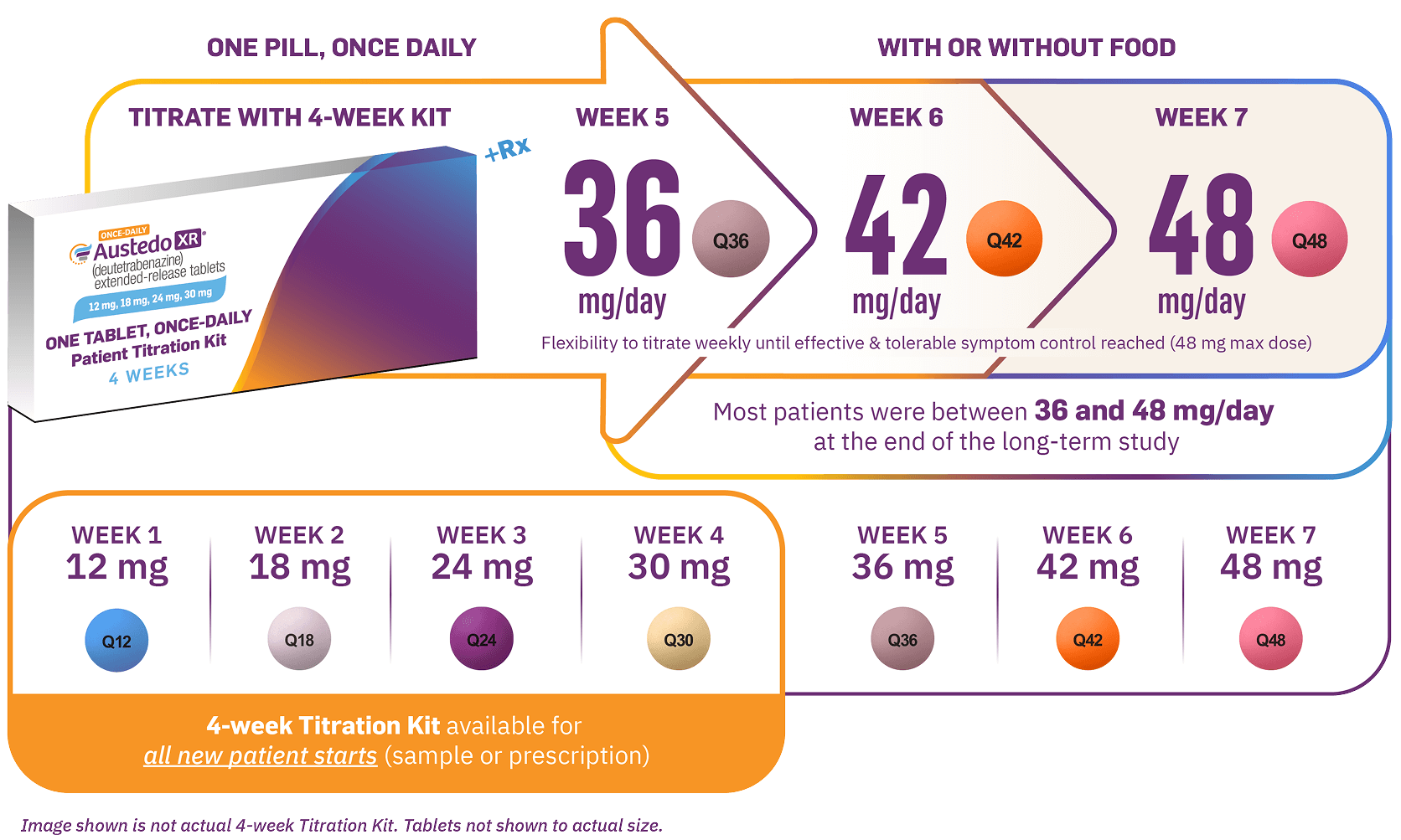
AUSTEDO XR has the most once-daily dosing options of any VMAT2 inhibitor.11,18 The recommended starting dose of AUSTEDO XR for patients with TD is 12 mg/day, which may be increased at weekly intervals by 6 mg/day until desired symptom control is tolerably achieved.11 The average daily dose in clinical trials was >36 mg/day, and 52% of patients were taking between 36 mg/day and 48 mg/day at Week 145 in the long-term study.12,14 AUSTEDO XR should be swallowed whole. Tablets should not be chewed, crushed, or broken. AUSTEDO XR may be taken with or without food (Figure 6).11
- The APA guidelines recommend VMAT2 inhibitors for the treatment of TD that has an impact on the patient, regardless of the severity of movements9
- AUSTEDO XR is a once-daily VMAT2 inhibitor approved for the treatment of adults with TD11
- Significant and meaningful symptom reduction was demonstrated with AUSTEDO and increased improvement over 3 years was seen in the OLE study, with 71% of patients at Week 145 experiencing improvement relative to Week 156,14
- The most common adverse reactions for AUSTEDO (3% and greater than placebo) in controlled clinical studies in patients with TD were nasopharyngitis and insomnia
- Adverse reactions with AUSTEDO XR are expected to be similar to AUSTEDO11
- In a real-world survey, patients reported improved social and emotional well-being as a result of movement reduction with AUSTEDO XR16
- The flexible, once-daily dosing possible with AUSTEDO XR allows for individualized treatment to achieve effective and tolerable control11
1. Caroff SN, Yeomans K, Lenderking WR, et al. RE-KINECT: a prospective study of the presence and healthcare burden of tardive dyskinesia in clinical practice settings. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2020;40(3):259-268 2. Jackson R, Brams MN, Citrome L, et al. Assessment of the impact of tardive dyskinesia in clinical practice: consensus panel recommendations. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2021;17:1589-1597. 3. Jackson R, Brams MN, Carlozzi NE, et al. Impact-Tardive Dyskinesia (Impact-TD) scale: a clinical tool to assess the impact of tardive dyskinesia. J Clin Psychiatry. 2022;84(1):22cs14563. 4. Finkbeiner S, Konings M, Henegar M, et al. Interim analysis of a patient-reported impact measure in the IMPACT-TD Registry. Presented at: Annual Psych Congress Elevate; May 30-June 2, 2024; Las Vegas, NV. Poster 5. 5. Carbon M, Hsieh CH, Kane JM, Correll CU. Tardive dyskinesia prevalence in the period of second-generation antipsychotic use: a meta-analysis. J Clin Psychiatry. 2017;78(3):e264-e278. 6. Data on file. Teva Neuroscience, Inc. Parsippany, NJ. 7. McCutcheon RA, Keefe RSE, McGuire PK. Cognitive impairment in schizophrenia: aetiology, pathophysiology, and treatment. Mol Psychiatry. 2023;28(5):1902-1918. 8. Jain R, Ayyagari R, Goldschmidt D, Zhou M, Finkbeiner, Leo S. Impact of tardive dyskinesia on physical, psychological, social, and professional domains of patient lives: a survey of patients in the United States. J Clin Psychiatry. 2023;84(3):22m14694. 9. American Psychiatric Association. The American Psychiatric Association Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients With Schizophrenia. 3rd ed. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 2021. Accessed February 7, 2025. https://psychiatryonline.org/doi/pdf/10.1176/appi.books.9780890424841 10. Solmi M, Pigato G, Kane JM, Correll CU. Treatment of tardive dyskinesia with VMAT-2 inhibitors: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018;12:1215-1238. 11. AUSTEDO XR® (deutetrabenazine) extended-release tablets/AUSTEDO® current Prescribing Information. Parsippany, NJ: Teva Neuroscience, Inc. 12. Anderson KE, Stamler D, Davis MD, et al. Deutetrabenazine for treatment of involuntary movements in patients with tardive dyskinesia (AIM-TD): a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Psychiatry. 2017;4(8):595-604. 13. Fernandez HH, Factor SA, Hauser RA, et al. Randomized controlled trial of deutetrabenazine for tardive dyskinesia: ARM-TD study. Neurology. 2017;88(21):2003-2010. 14. Hauser RA, Barkay H, Fernandez HH, et al. Long-term deutetrabenazine treatment for tardive dyskinesia is associated with sustained benefits and safety: a 3-year, open-label extension study. Front Neurol. 2022;13:773999. 15. Hauser RA, Barkay H, Fernandez HH, et al. Deutetrabenazine provides long-term benefit for tardive dyskinesia regardless of underlying condition and dopamine receptor antagonist use: a post hoc analysis of the 3-year, open-label extension study. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2024;44(4):386-396. 16. Jain R, Konings M, Thompson S, Yang A, Kotak S, Gandhi P. Real-world evidence of patient experience with once-daily deutetrabenazine extended-release tablets for tardive dyskinesia and chorea in Huntington disease in the United States. Presented at: Annual Psych Congress; October 29-November 2, 2024; Boston, MA. 17. DrugBank Online. P-glycoprotein substrates. Accessed February 13, 2025. https://go.drugbank.com/categories/DBCAT002668 18. Ingrezza® (valbenazine) capsules. Prescribing Information. San Diego, CA: Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc.










